Homepage / Bullion Investment Basics: Bullion Glossary
Last Updated on 01/28/2025
Bullion Glossary
Bullion glossary terms related to the physical and liquid
bullion market.
"Click" the Letter, to go directly to Definitions starting with it.
ExpressGoldCash - 4.9 star - Customer Reviews
Bullion Glossary
A
Active Delivery Month - The quoted delivery month on the most frequently traded futures contract on a futures exchange. Spot prices will be derived from the contract price for the active delivery month.
Ag - is the chemical element symbol for silver on the periodic table
Alloy - mixing two or more chemical elements, including at least one metal. (Ex: Gold is often mixed with a base metal or metals to add durability or influence the color.
ANA - American Numismatic Association
Ask Price - The lowest quoted price a bullion dealer or coin dealer will sell a item.
Assay - the testing of a precious metal to determine its weight and purity.
Assayer - someone who tests precious metals to determine its purity.
Assay Mark - the stamp from a assayer on a bullion bar of a precious metal to guarantee its purity.
Assay Office - An official organization controlling the testing of precious metals within a country
Au - is the chemical element symbol for gold on the periodic table
Bullion Glossary
B
Backwardization - A market situation in which prices are progressively lower in future months than in the nearest month,caused by shortage or tightness in supply.
Bank of England - Founded in 1694. has been the focal point of gold and silver trading in London for over three centuries.
Base metals - Metals that are not precious
Bear Market - A market in which the trend is for prices to move lower.
Bid Price - The quoted price a dealer will pay for bullion or coins
Blank - is a blank disc of metal with milled edges used to make a coin
Bretton Woods
Brilliant Uncirculated Coin - A generic term applied to any coin that has not been in circulation.
Broker - an agent between buyers and sellers between the buyers and sellers of securities or property.

Bullion - Precious metals in the form of coins, bars, and or rounds in a investment trading form. Consists of 999.0 purity or finer.
Bullion Bank - is a members of the LBMA (London Bullion Market Association); they are investment banks that function as wholesale suppliers dealing in large quantities of gold.
Bullion Bars / Ingots - Investment Bullion bars come in troy weight measurement. Private mints and refiners produce bullion bars.
Bullion Coin - A precious metal coin, generally minted by governments.
Bull Market - A market in which the trend is for prices to increase.
Bullion Rounds - Rounds that are similar to coins in shape, they are produced by private mints and refineries and have no status as legal tender. Rounds can be created to commemorate a person, place or an event.
By-Product - A secondary mineral from a mine, refinery or a secondary refinery.

Bullion Glossary
C
Carat - The carat is a unit of mass equal to 200 mg (0.007055 oz), and it is used for measuring gemstones and pearls. (Sometimes confused with "karat" which is used to measure the purity of gold)
Cast Bars - have a lower quality finish and are produced by pouring molten precious metal directly into a mold.

Central Bank - A central bank is also known as a reserve bank or monetary authority, is a government institution that usually issues the currency, regulates the money supply, and controls the interest rates of a country. Central banks also oversee the commercial banking system of their respective counties.
Ex: European Central Bank, Bank of Japan, Bank of Canada
Chip-Gold - consists of a small ingot (1-20 grams) in a sealed and certified package the size of a credit card.
Choice Uncirculated - coin grading term, An above average coin that may have a few light marks.
CME Group Inc. - Chicago Mercantile Exchange - is the world's largest futures exchange company.
Coin - is a term used for government issued legal tender coins. This is why the term "round" is used for privately produced coins.
Clad or Cladding - a method to bond two metals together, often used to bond a higher priced metal to a lesser one. The United States Mint uses cladding to manufacture coins. (Ex:Current US Penny 2.5% copper/97.5% zinc)
Coining Press - The minting machine that strikes coins
COMEX - is a division of the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX), the worlds largest physical commodities futures exchange.
Commodity - Raw materials that can be bought and sold, A transportable article of commerce, or trade. ex: gold, silver, corn, coffee, sugar or wheat.
Cull - A coin that is worn to the point of being barely identifiable.
Cu - is the chemical element symbol for copper on the periodic table

Bullion Glossary
D
Deflation - A phase of the business cycle during which consumer spending is seriously curtailed, bank loans contract and the amount of money in circulation is reduced.
Delivery - The tender of the actual commodity such as silver or gold against a short position in futures during the period allowed by the futures contract
Die - A piece of metal engraved with a design, used for stamping coins
Doubled die - a term in used to refer to doubling in the design elements of a coin.
Double Bottom - a technical expression indicating that the general market, commodity or individual stock has twice declined to, but failed to penetrate, the approximate lowest level reached during the preceding reaction. (The same principle is applied to a triple bottom)
Double Top - reverse of double bottom, indicates when the general market, commodity or individual stock has twice moved up, but failed to penetrate, the approximate highest level reached during the preceding reaction. (The same principle is applied to a triple top)
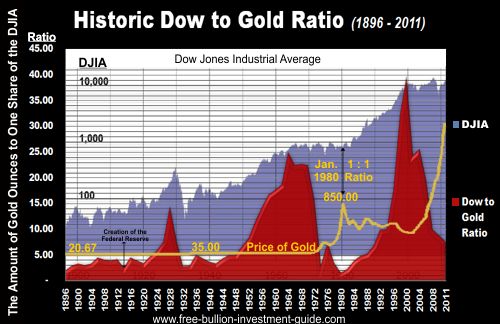
Dow to Gold Ratio - is the amount of Gold Ounces it takes to buy one share of the Dow Jones Industrial Average.
Bullion Glossary
E
E Pluribus Unum - The Latin motto found on all U.S. coins, which means "Out of many, one".
Executive Order 6102 - is an Executive Order signed on April 5, 1933, by U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt. The Executive Order required all U.S. citizens to turn in all but a small amount of gold coins, gold bullion, or gold certificates owned by them, to the Federal Reserve. For every ounce of gold returned a citizen would receive $20.67.
Executive order 11825 - is an Executive Order signed on December 31, 1974, by U.S. President Gerald Ford. It repealed President Franklin D. Roosevelts Executive Order 6102 forbidding U.S. citizens to own gold. Shortly thereafter, in 1977, the U.S. Congress passed a law forbidding any president to confiscate gold from U.S. citizens, except during a time of war.
Exchange - A meeting place for buyers and sellers of securities, or commodities. An unincorporated membership association the members of which trade securities or commodities, for themselves or others.
Extruding Bullion Bars - Process in which a metal or other material is forced through a series of dies to create desired shape or shapes. Markings are usually stamped on the bar using a hammer or a press.
ExpressGoldCash - 4.9 star - Customer Reviews
Bullion Glossary
F
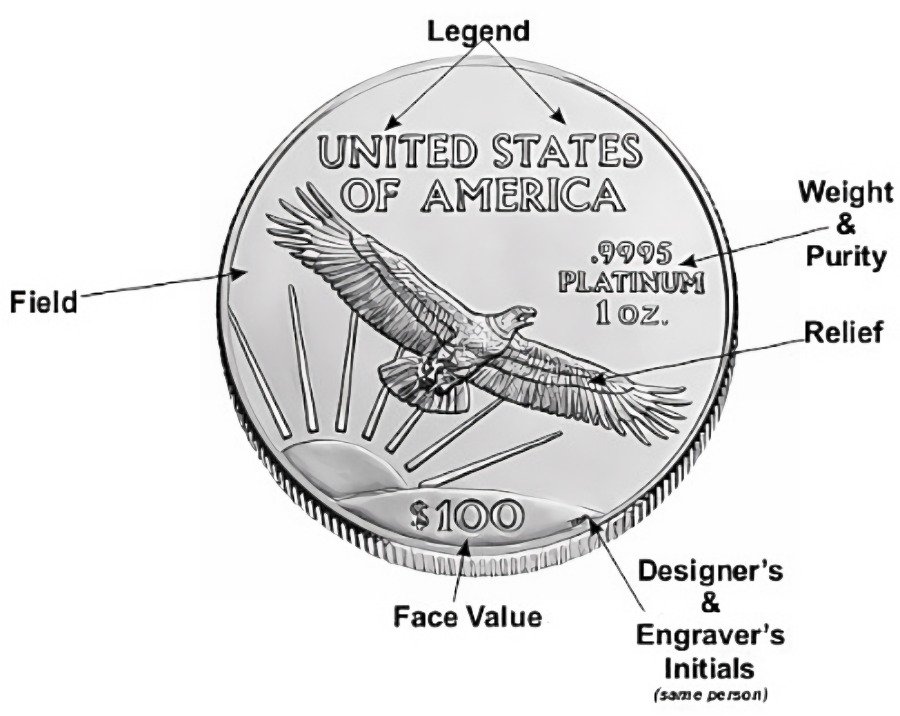
Face Value - The legal tender value of a coin inscribed on the face of a coin. (or stamp, stock certificate, bond, etc.)
Federal Reserve System of the United States
Fiat money or Fiat Currency - currencies that are not restrained by being pegged to tangible assets such as gold reserves. Today, all national currencies are fiat currencies.
Fineness - A measure of the purity; represents the purity of precious metals, either in monetary or bullion form.
Fine Weight - The weight of a precious metal contained in a bullion bar, coin or round as determined by multiplying the gross weight by the fineness.
Flan - A blank piece of metal in the size and shape of a coin; another term for a planchet or blank.
Fundamentals - The study of basic underlying economic factors which apply to the state of business.
Futures - A commodity contract is a commitment that requires delivery or receipt of a commodity at an agreed future date, at an agreed price established by public auction in the trading pit of an organized public commodity exchange

Apples of Gold - Customer Reviews - 4.9 stars
Bullion Glossary
G
Gold Confiscation - also known as the executive order 6102 of 1933. It was an executive order signed by U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt forbidding every U.S. citizen to own gold.
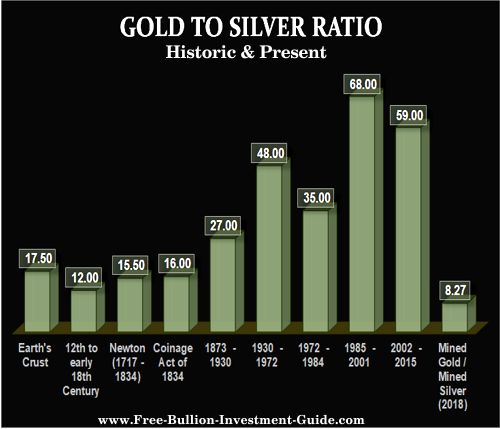
Gold/Silver Ratio - The amount of silver ounces it takes to buy one ounce of gold.
Gold Standard - A monetary system with a fixed price for gold. Furthermore, gold is either the whole circulation of currency within a nation or is supplied with notes representing and redeemable in gold.
Government Issued Bullion Coins - the oldest form of coinage, modern bullion coins come in all precious metals from a government mint. Modern bullion coins are purchased both as bullion and for their collectible, numismatic value
Graded Coin - A coin authenticated and graded by a neutral or impartial, third party professional service
"Gresham's Law" - named after Sir Thomas Gresham (1519–1579).
Gresham's Law is a monetary principle stating that "bad money drives out good." Money that has intrinsic value because it contains a precious metal will be over-valued and will leave the country or disappear from circulation due to hoarding. While money that has no intrinsic value and is made of base metals or easily manufactured commodities is undervalued and will flood into circulation.
Grain - One of the earliest units of weight for gold; one grain being the equivalent of one grain of wheat. 1 grain = 0.0648 grams or 0.002083 troy ounces. (See the Troy page for more troy weight conversions)

Bullion Glossary
H
Hedging - A hedge is a position established in one market in an attempt to offset exposure to price changes or fluctuations in some opposite position with the goal of minimizing one's exposure to unwanted risk. Ex: If you were to buy bullion today, you would be hedging your money to any future losses in the dollar.
Hunt Brothers

BGASC - Customer Reviews - 4.8 stars
Bullion Glossary
I
IMF - The International Monetary Fund - was conceived at the Bretton Woods Conference in 1944 to promote international monetary co-operation and stability.
Inflation - is the increase in the money supply, which causes goods and services to increase in price. Inflation is the inflating of the money supply or the excessive printing of money.
Ingot - a material, usually metal, that is cast into a shape suitable for further processing
Intrinsic Value - (melt value) is the value of the precious metal content in a coin or bar.
IRA - individual retirement account ( Also see Roth IRA)
Bullion Glossary

J
Junk Silver Coins - is a silver bullion market term used for any silver coin which has no numismatic or collectible value above the value of the silver it contains.
Free Shipping on Orders $199+ | 5.0 star Customer Reviews
Bullion Glossary
K
Karat - The karat (symbol kt) a unit of measure of the amount of pure gold in a metal. One karat represents 1/24th of an alloy’s total weight. One hundred percent gold is 24 karats.
24-karat gold = 999.0 to 999.999 (per mille)
22-karat gold = 916.0
18-karat gold = 750.0
14-karat gold = 583.0
10-karat gold = 416.7
Keynesian economics - also known as Keynesianism or Keynesian theory, named after Lord John Maynard Keynes (born June 5, 1883 & died April 21, 1946) he was a British economist whose practices and ideas have affected the theory and practice of modern economics. Keynesian economics argues that the private sector activities sometimes lead to inefficient macroeconomic outcomes and therefore advocates active policy responses by the public sector (government). This includes monetary policy actions by a central bank or reserve bank and fiscal policy actions by the government to stabilize output over the business cycle.
Key Date - The rarest or one of the most rare and therefore most expensive members of a coin series. For example, 1916-D Mercury dime.
Krugerrand - South African gold coin first issued in 1967, it has a purity of 916.6
Bullion Glossary
L
LBMA - London Bullion Market Association, incorporated in 1987, to represent the interests of the participants in the wholesale bullion market.
Lease Rate - An interest rate charged for borrowing.
Leaching - the extraction of a soluble metallic compound from ore by dissolving the metals in a solvent
Legal Tender - Money that is officially issued and recognized for redemption by an authorized agency or government
Limit order - An order to buy or sell at a price that is better (higher or lower) than the current market.
Liquid Assets - Assets consisting of cash or other property which can be readily converted into money
Liquidity - a condition existing when an investor or a business holds onto assets which can be readily converted into cash with little loss in value
London Auction Price - Sometimes referred to as the 'auction'. the London Metal Exchange (LME) administers the London Bullion Market Association (LBMA) precious metals price auctions. These prices are set twice daily; the first at 09:45 (am price) and the second at 14:00 (pm price) London time. These prices are published benchmarks. The auction price is a bid price for good delivery ingot or plate, located in vaults in London or Switzerland. Hence it is the price which auction members would be prepared to pay for precious metals in the form of plate or ingot deposited in a London or Swiss vault. Customers can instruct dealers to buy or sell metal at the auction price but they will incur charges for brokerage, conversion and transportation. Customers do not have the benefit of knowing what the price is before they buy or sell.
Long Position - The position of owning a commodity or security.
LPPM - London Platinum and Palladium Market.
ExpressGoldCash - 4.9 star - Customer Reviews
Bullion Glossary
M
Margin - The amount of money and / or securities deposited by a client with a broker to finance part of the cost of purchasing.
Margin Account - A brokerage account wherein listed securities may be purchased with the aid of credit provided by the buyer's broker.
Margin Call - A demand made by a broker upon his/her client to advance money or securities either to finance an initial purchase or to maintain the minimum margin requirements set by the stock exchange or the brokerage firm or both.
Market Instinct - The ability to interpret with reasonable accuracy, the true meaning and significance of price movements and volume changes and their relationship.
Market Value - The actual monetary value which an bullion coin, round or bar possesses in itself.
Milled Coinage - also known as machine-struck coinage is used to describe coins which are produced by some form of machine.
Milled Edge - A raised rim around the outer surface of a coin.
Milling Mark - A mark resulting from the reeded edge of one coin hitting the surface of another
Mint - A manufacturing facility for producing coins.
Mintage - Total number coins minted, for individual coins
Minted Bullion Bars: are cut from a cast bar that has been rolled to a uniform thickness. The cutting is done with a die to create blanks
that have a specified dimension and weight. All the surfaces are smooth and even. Markings are usually stamped on the bar, using a minting press.
Minter’s Die - A piece of very hard metal on which the design is engraved as hollows or reliefs, which will be reproduced on a blank in the minting process.

Mint State - A grade of a business strike coin that has never been in circulation. It may have many marks, or none at all.
Mint Mark - Letter or symbol of the mint which produced the coin
Moving Average - a trend line that is plotted on a chart, reflecting the price over a given period of time
MS - Abbreviation for Mint State coin.
Bullion Glossary
N
Nixon Shock of 1971 - was a series of economic measures taken by U.S. President Richard Nixon in 1971 including unilaterally canceling the direct convertibility of the United States dollar to gold.
Nugget - a small or large piece of a precious metal found in nature.

Numismatics - The art and science relating to the study of coins, tokens, medals, paper money.
Numismatist - One who is knowledgeable in the area of numismatics.
NYMEX - is the largest physical commodity exchange in the world. A United States futures exchange consisting of two divisions, NYMEX (the New York Mercantile Exchange) and COMEX (the Commodities Exchange)
Bullion Glossary
O
Obverse side of a coin - The front or heads side of a coin
Offer price - Lowest price at which a dealer is willing to sell a commodity or security (alternative term to ask).
Open interest - The number of open or outstanding contracts on a futures exchange for which the holders are still obligated to the futures exchange concerned. No offsetting sale or purchase has yet been made against it. Open interest is used as an indicator of the level of commercial activity in a particular futures contract.
Open position - A long or short trading position that is not yet closed. In either case the dealer remains vulnerable to fluctuations until the position is closed.
Option - An agreement, which conveys the right to buy or sell a specific security, property or commodity at a specific price within a stated period of time.
Over-strike - An impression made with different dies on a previously struck coin.
Bullion Glossary
P
Pd - is the chemical element symbol for palladium on the periodic table
Pegged Price - The price at which any commodity has been fixed (pegged) by agreement, custom or law.
Penny-Weight - widely used as a unit of weight in the jewelery trade in North America. (20 pennyweights = 1 troy ounce)
Perfect Uncirculated - coin grading term, bullion coins with a grade of MS-70 are in Perfect condition.
Planchet - The blank disk of metal on which a design is stamped to become a coin
Plate - Bullion for of metal.
Platinum Group Elements / Metals (PGE/PGM) - six metallic elements consisting of platinum, palladium, rhodium, ruthenium, iridium and osmium.
Precious Metals - are rare, natural metallic chemical element of high economic value. Precious metals have been used as currency, but are now regarded mainly as investment and industrial commodities. Gold, silver, platinum, and palladium are each recognized to be in this category.
Precious Metal Lease Rate - An interest rate charged for borrowing precious metal.
Premium (Bullion Coins, Bars & Rounds) – The added market value of a bullion coin, round or bar that exceeds the item precious metal spot price. The premium includes the costs of production, and dealer fees.
Premium (Numismatic/Collector Coins) - Collector or Rare coins usually carry higher premiums representing the coin's numismatic value. A Collector's Premium is based on supply or scarcity (mintage), demand from other Collectors for the coin, quality of the coin, and other intangible factors.
Prime Investment - a first class, high grade investment
Proof Coin - is a coin made with a specially polished acid treated die, the background design of the coin die is polished, resulting in a mirror-like finish on the coin it strikes and a frosted finish on the raised portions of a coin.
Pt - is the chemical element symbol for platinum on the periodic table
Bullion Glossary
Q
Quartation - The process in which silver is separated from gold by dissolving it out with nitric acid, commonly known as, nitric acid parting.
Bullion Glossary

R
Rarity - Generally relates to the scarcity or relative unavailability of a coin.
Ratio - The relationship between one number to another, obtained by dividing the first by the second.
Reeded Edge - The edge of a coin with grooved lines that run vertically around its perimeter.
Refining - the separating and purifying precious metals or base metals
Relief - The portion of a coin design that is raised above its surface.
Reverse side of a coin - The back or tails side of a coin.
Round - A round is a precious metal disk issued by a private entity and is not intended for circulation. A round does not have legal tender status and is not backed by a government.
Roth IRA - Named after its chief legislative sponsor, the late Senator William Roth of Delaware. The Roth IRA is a special type of retirement plan under US law that is generally not taxed. The main difference from a Roth IRA and most other IRA plans is that once the participant retires they are not taxed on the money withdrawn from the plan.

BGASC - Customer Reviews - 4.8 stars
Bullion Glossary
S
Scrap Gold - a term for any form of gold which is sent to a refiner or processor for recycling
Sheldon Scale - is the grading system used for coins, named after William Sheldon who standardized coin grading in 1948. The Sheldon scale helps dealers, collectors and investors determine a coins' value. See the Graded Bullion page for more information.
Short Account - securities which have been sold short with the anticipation of the stock declining in price
Short Covering - The act of buying back a commodity, security or opposing futures contract to close out a short position.
Short Position - Position resulting from a short selling strategy.
Short Sale - any transaction which creates a debt in terms of promised goods. Example in stock terms: selling a number of shares to make delivery to the purchaser, in hopes of buying back the stock for a return to the lender at a lower price.
Note: Understanding Short Selling can be very confusing. The video below gives a good description on; "How a short sell transaction takes place." (This video is here for educational purposes only)
"What is Short Selling?"Silver - Latin name Argentum, Ag is the chemical symbol, relative density is 10.5 and the melting point 960°c

Silver Certificate - Paper money that was once redeemable for its face value in silver.
Slab - a sealed hard plastic holder used by third party professional grading services to house coins they have determined to be authentic.
Smelting - a process of melting ores or concentrates to separate out precious metals from any impurities.
Spot price - or spot rate is the current price of an asset, bought or sold, for immediate delivery.
Spread – The difference between the buy price and the sell price.
Sterling Silver - Sterling silver is a composition of 925 parts pure silver with 75 parts of copper
Strike - The process of stamping a design into a planchet or blank by force with a die to create a coin
ExpressGoldCash - 4.9 star - Customer Reviews
Bullion Glossary
T
Tael - Traditional Chinese unit of weight for gold. 1 tael = 1.20337 troy ounces = 37.4290 grams.
Tola - Traditional Indian unit of weight for gold. One tola = 0.375 troy ounces = 11.6638 grams. 10 tola = 3.75 troy ounces
Toning - toning is formed on a coin as a result of the metal interacting with the environment over time
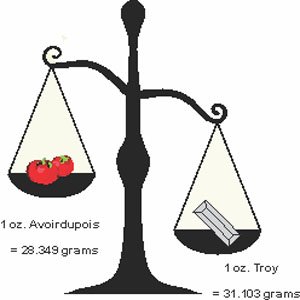
Troy Ounce - (ozt.) - a measurement system of weight, used for precious metals, gemstones and gunpowder.
Bullion Glossary
U
Uncirculated Coin - a coin that was not issued for circulation.
US Dollar Index - (USDX) - is an index to measure of the value of the United States dollar relative to a basket of foreign currencies.
- Euro (Euro) 57.6% weight
Pound sterling (GBP) 11.9% weight
Canadian dollar (CAD) 9.1% weight
Swedish krona (SEK) 4.2% weight and
Swiss franc (CHF) 3.6% weight.
Japanese Yen (JPY) 13.6% weight.

Bullion Glossary
V
Value Date - The date on which a commodity is delivered to an account and usually when payment is due (unless other payment date arrangements are made between the relevant parties).
Bullion Glossary
W
Wafer - a thinner and flatter, stamped bullion bar also known as a biscuit
Ware-House Receipt - a depository receipt issued when delivery is taken on a futures exchange. The receipt specifies the quantity and fineness of gold or silver sold.
White Gold - most often used in the jewelery industry, it is a alloy containing a agent to whiten the gold such as silver, platinum, palladium or nickel.

Bullion Glossary
X
Bullion Glossary
Y
Yield Curve - The relationship between interest rate yields and maturity lengths. The curve shows the relation between the (level of) interest rate (or cost of borrowing) and the time to maturity, known as the "term", of the debt for a given borrower in a given currency. Investors expect a higher return for holding an asset for a longer time, hence yields normally increase with maturity length.
Free Shipping on Orders $199+ | 5.0 star Customer Reviews
Bullion Glossary
Z
Other pages, on this Guide, that you
may like...
|
|
|
Bullion Glossary
OR
For Bullion Market News...
|
Support this Guide & Paypal Thank You for Your Support |
|
|
 | |||||
Free Bullion Investment Guide
Keep this Guide Online
& Paypal
Thank You for
Your Support
Search the Guide
| search engine by freefind | advanced |

Daily
Newsletter
Mintages
for
2024
Gold & Silver Mexican Libertad
|
Gold Libertads |
Chinese Gold Coin Group Co.
& Chinese Bullion
2025
Gold & Silver Chinese Panda
|
Silver Panda |
Help Us Expand our Audience by forwarding our link
www.free-bullion-investment-guide.com.
Thank You!
March's

All Articles were Originally Posted on the Homepage




ExpressGoldCash - 4.9 star Customer Reviews

18W LED Security Light (Dusk to Dawn & Motion Sensor) - $32.99
from:
 LED Lighting
LED Lighting