Homepage / Bullion Coins: Russian Bullion
Last Updated on 03/22/2025
The Bank of Russia
&
Russian Bullion
The Bank of Russia (known in Russia as "Bank Rossii") is the Central Bank of the Russian Federation; it has exclusive rights to issue Russian currency, commemorative and circulated coins, and investment-grade precious metal bullion coins.
Early History
of the Russian Central Bank
The Bank of Russia has undergone several name changes and alterations due to the changes in the Russian government.
The State Bank of the Russian Empire, the first central bank in Russia, served as the dominant financial institution from 1860 until the end of the Russian Empire in 1917.
On 7 November 1917, the first day of the October Revolution, an armed detachment under direct orders from Vladimir Lenin occupied the State Bank's head office. In December and January, all of Russia's commercial banks were nationalized and forcibly merged into the State Bank, with their shareholders wiped out; the State Bank was renamed the People's Bank in May 1918.
The People Bank was liquidated in January 1920. No banks were formally recognized in the country until the second central bank of Russia was created and called the State Bank of the USSR, commonly referred to as Gosbank, in October 1921.
The End of the Soviet Union (USSR)
and it's State Bank
The State Bank of the USSR was founded in 1921 and ended in 1991 after the Soviet Union (USSR) collapsed.
Before the breakup of the USSR, the State Bank of the USSR was accountable only to the Supreme Soviet of the Russian SFSR (Soviet Federative Socialist Republic - the largest and most influential republic in the former Soviet Union).
The "Supreme Soviet" was a permanent legislative body of the Soviet Union; each republic of the USSR also had its own Supreme Soviet.
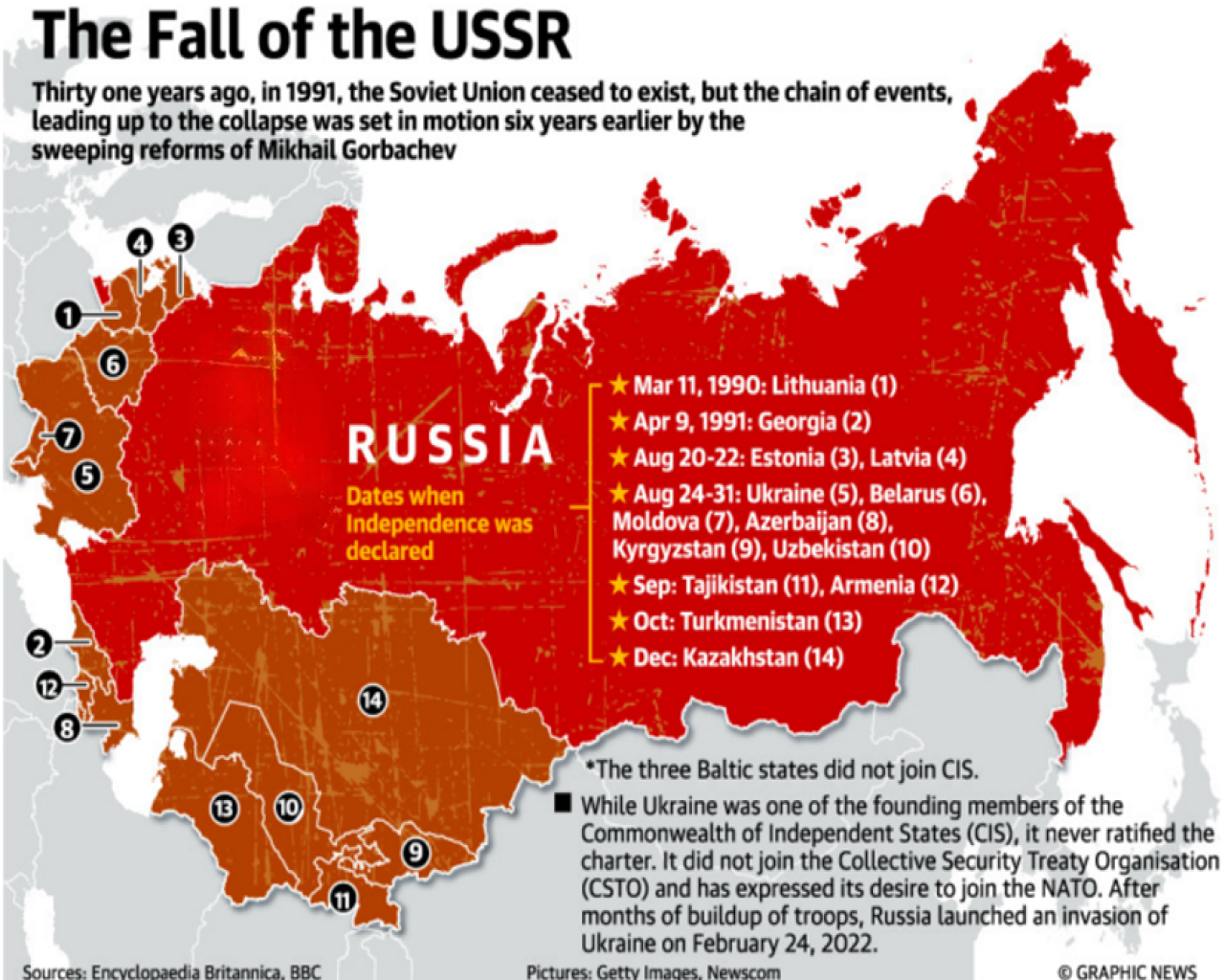
In the late 1980s and early 1990s, the USSR (Union of Soviet Socialist Republics) was experiencing a power struggle. After Mikhail Gorbachev became the General Secretary of the Communist Party on March 11, 1985, he aimed to reform the Soviet Union, which was burdened by the social and economic limitations of its communist system. Gorbachev named his reforms "Perestroika."
Gorbachev's efforts to reach out to the United States and Britain to end the Cold War were popular internationally, but at home, his popularity was waning. Gorbachev attempted to decentralize the economy while maintaining a strong government control, similar to China's current system, but faced numerous detractors, hindering his plans.
In 1989, cracks in the strength of the Soviet Union (USSR) began to show when Gorbachev declined to intervene militarily when Warsaw Pact countries, including East Germany, started to abandon the Soviet Union (USSR) by breaking away from communism and Marxism.
This was the start of the Revolution of 1989.
In June 1990 the Congress of the Russian republic proclaimed that the Russian Federation's (Russia's largest republic) laws took precedence over Soviet laws, and the following year Boris Yeltsin became the Russian Federation's first democratically elected president.
A coup was attempted in August 1991 by hard-line communists opposed to Gorbachev’s reforms, which led to the collapse of most Soviet government organizations, the abolition of the Communist Party’s leading role in government, and the dissolution of the party itself.
In the following days and months of the failed coup, many republics declared independence. The Baltic state of Lithuania was the first to secede from the Soviet Union in March 1990 when it proclaimed the restoration of its independence.
The State Bank of the USSR was dissolved on December 20, 1991. All its assets, liabilities, and property were transferred to the Central Bank of the Russian Federation (Bank of Russia).
On 24 December, the Russian Federation took the Soviet Union's seat in the United Nations.
On December 25, 1991, Gorbachev resigned as the leader of the Soviet Union and turned over his powers, including control of the nuclear launch codes, to Boris Yeltsin, who was now the first president of the Russian Federation. (Vladimir Putin would succeed him on December 31, 1999 after Yeltsin unexpectedly resigned.)
On December 26, 1991, the Soviet Union was formally dissolved and the Russian Federation was established as an independent country.
Central Bank of the
Russian Federation
The Bank of Russia (Bank Rossii) is the central bank of the Russian Federation.
Shortly after declaring sovereignty in June 1990, the Russian Federation legislated the creation of a central bank, naming Georgy Matiukhin as its leader. Matiukhin took control of all branches of the State Bank of the USSR and consolidated its operations under the new Bank of Russia.
After the disbandment of the State Bank of the USSR, the Bank of Russia created a new chart of accounts and established a network of cash settlement centers for the Bank of Russia to establish and set up the official exchange rates of foreign currencies against the Russian ruble.
The Bank of Russia's functions are written in the Constitution of the Russian Federation "Article 75."
According to the constitution, the Bank of Russia is an independently run entity with the primary responsibility of protecting the stability of the national currency, the ruble.
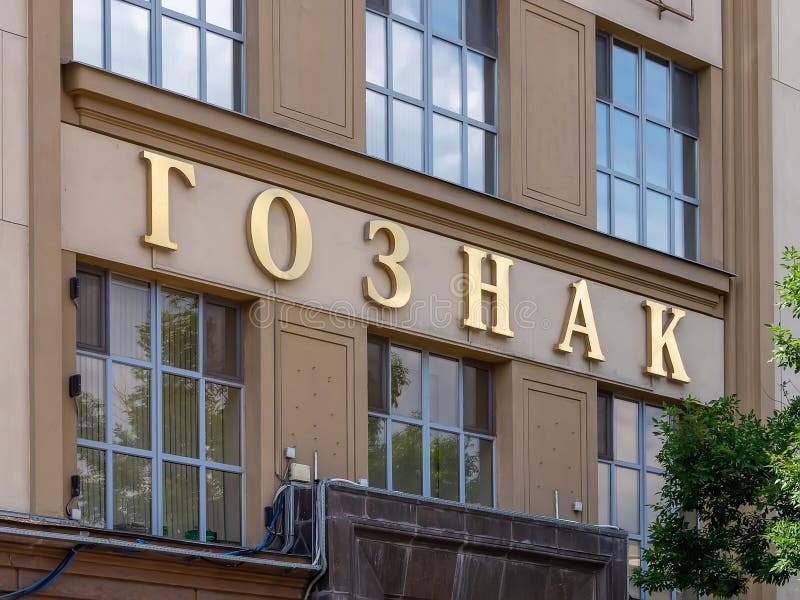
The Bank of Russia is responsible for issuing Russian ruble banknotes, commemorative coins, and investment-grade precious metal bullion coins, and it does it through a special government entity known in Russia as the Goznak.
Goznak
Gonzak is the name of the institution in Russia that is in charge of producing all of the country's banknotes, medals, coins, and stamps; it also provides its services to many international clients.
Goznak is Russian for "State Ensign or Insignia." The Goznak was established in 1818, upon the order of Alexander I; it printed the first postage stamp and published unique book editions, as well as minted numerous commemorative coins and medals.
The Goznak has transformed from a state-run governmental institution into an open joint-stock company, although all its shares remain with the state. The Goznak issued the first Russian Federation coins in 1993.
Goznak includes 8 branches: 2 Mints, 2 Printing Factories, 2 Paper Mills, Printing House and R&D Institute.
- Saint Petersburg Mint
- Moscow Mint
- Perm Printing Factory
- Moscow Printing Factory
- Saint Petersburg Paper Mill
- Krasnokamsk Paper Mill
- Moscow Printing Works
- Research Institute of Goznak (in Moscow)
In addition to Russia, the Goznak provides coins and banknotes for many countries in Central and South America, Southeast Asia, the Middle East, Africa, and some former Soviet republics.
Russian Mints
Saint Petersburg Mint (formerly Leningrad Mint)
In 1703, Peter I, the first Emperor of Russia, founded St. Petersburg. The city is named after Saint Peter the Apostle and served as the capital of the Russian Empire from 1721 to 1917. The city is situated in Northwestern Russia, along Neva Bay, with the Neva River flowing through it.
In 1924, Saint Petersburg and its Mint changed its name to Leningrad after Vladimir Lenin's death. In 1991, shortly after the fall of the Soviet Union, the citizens of the city voted to change the name back to Saint Petersburg.
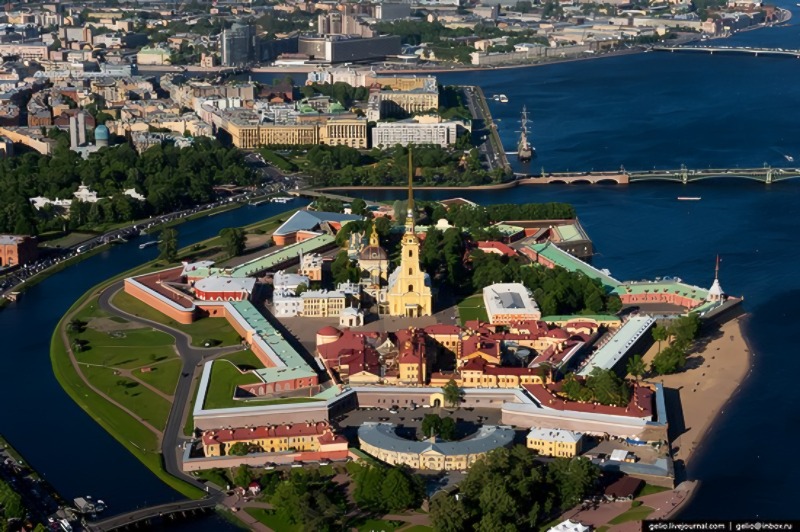
The Saint Petersburg Mint was founded by Peter the Great in 1724 and is one of the oldest enterprises in St. Petersburg. The mint consists of several buildings, all on the territory of Peter and Paul Fortress on Rabbit Island in the heart of the historic center of St. Petersburg.
Above, in the photo of the Peter and Paul fortress on Rabbit Island, the Peter and Paul Cathedral is featured with the red roofs of the St. Petersburg Mint in the foreground. Up until 2012, the cathedral was the tallest building in St. Petersburg, standing at 402 ft.
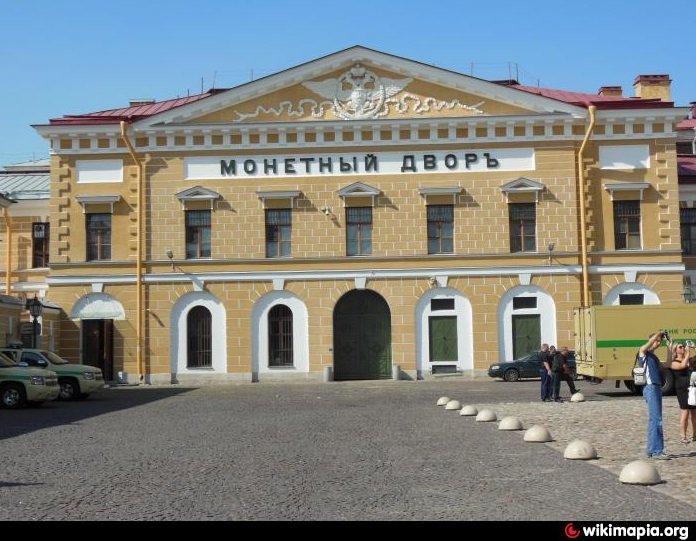
 Saint Petersburg Mint
Saint Petersburg MintHallmark/ID-mark
The main building of the Mint, shown above right, was designed in a strict classical Russian style and constructed between 1800 and 1805 within the eastern fortifications. Shortly after construction ended, advanced minting machines, including steam-powered Bolton coin-making machines, were installed in the main building.
In the 1830s and 1840s, more buildings were added to the main building of the St. Petersburg Mint, with the construction of many workshops all discernible from the rest of the buildings within the fortress by their red roofs.
Saint Petersburg Mint is one of the world's largest mints; its hallmark/id-mark uses the Russian letters СПМД (SPMD in English).
Today, the Saint Petersburg Mint is a modern enterprise with advanced machinery capable of producing coin and medal products of various geometrical configurations of non-ferrous and precious metals, adhering to international cold stamping quality standards, and striking coins weighing from 1.55 grams to 5000 grams.
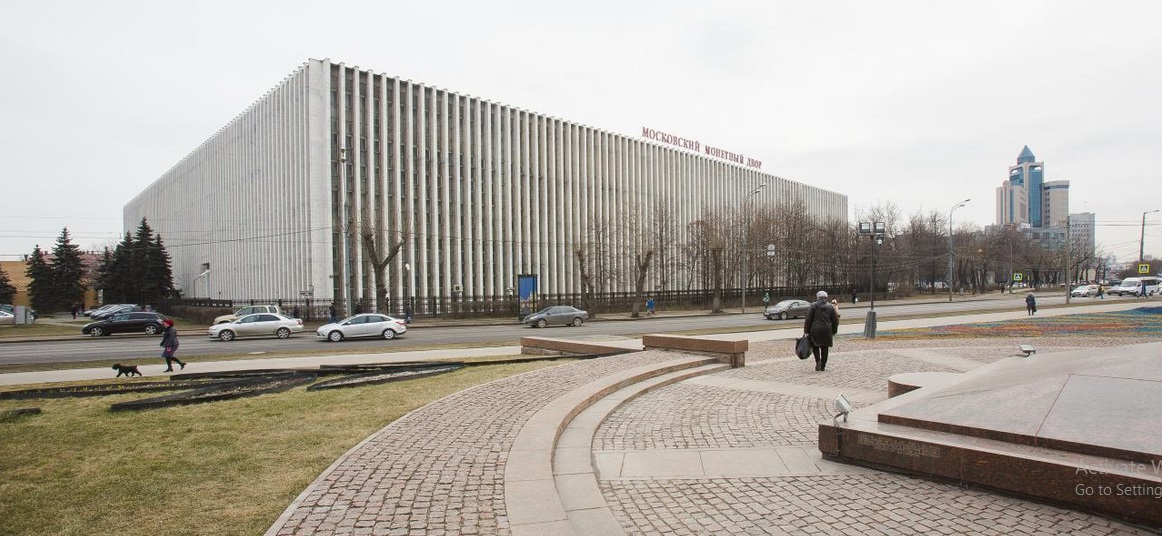
Moscow Mint
The history of coinage in Moscow dates back several centuries; it is said that its first mint was built in 1534 and operated until it closed in 1776. It wouldn't be until after Germany invaded the USSR during World War II and threatened Leningrad (St. Petersburg) that the country reopened a Mint in Moscow.
On April 25, 1942, the Moscow Mint opened after the St. Petersburg (Leningrad) Mint was closed and moved into the interior of Russia (Krasnokamsk) to protect it from the advancing German invasion forces. The relocated mint could not meet demand, so the USSR opened the Moscow Mint to fulfill the country's needs.
The Moscow Mint hallmark/id-mark uses the Russian letters ММД (MMD in English).
The Moscow Mint is a renowned enterprise that produces high-quality, unique coins of gold, silver, and base metals using advanced technologies and tools. It also produces subsidiary, commemorative, and investment coins of nonferrous metals under the Bank of Russia's orders and in other countries.
Historic Russian
Precious Metal Coins
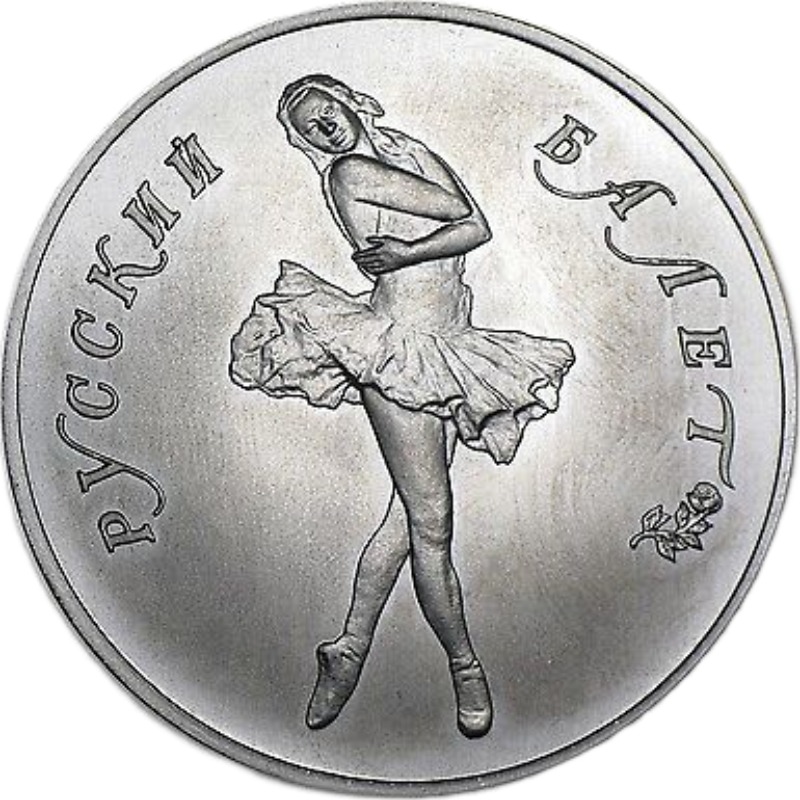
The Palladium Ballerina
The Russian Ballerinas palladium bullion coins are highly sought-after and known for their intricate design and rich history.
The commemorative coins honor the Bolshoi Ballet, a renowned Russian ballet company established in 1776, originating in Moscow and derived from the Russian words "Grand Ballet"
The Palladium Ballerina bullion coins were introduced by the Soviet Union in 1989, and they continued to mint them through 1991 at the St. Petersburg Mint (Leningrad).
The palladium bullion coins had a purity of 999‰ pure palladium and were minted in both proof and bullion versions.
When the Soviet Union introduced the palladium coin, they were only available in 1 oz. (31.10 grams, 25 rubles); then in 1990, two additional coins were made available: 1/2 oz. (15.5 grams, 10 rubles) and 1/4 oz. (7.78 grams, 5 rubles). (oz = Troy oz.)
No Russian Palladium Ballerina bullion coins were minted in 1992, likely because of all the turmoil surrounding the collapse of the Soviet Union.
In 1993, the Russian Federation restarted the production of the Palladium Ballerina bullion coin and continued to mint it in 1994 in proof and bullion versions of the coin in 1 oz., 1/2 oz., and 1/4 oz..
1995 was the last year the Palladium Ballerina bullion coin was minted, but only a proof version was made available.
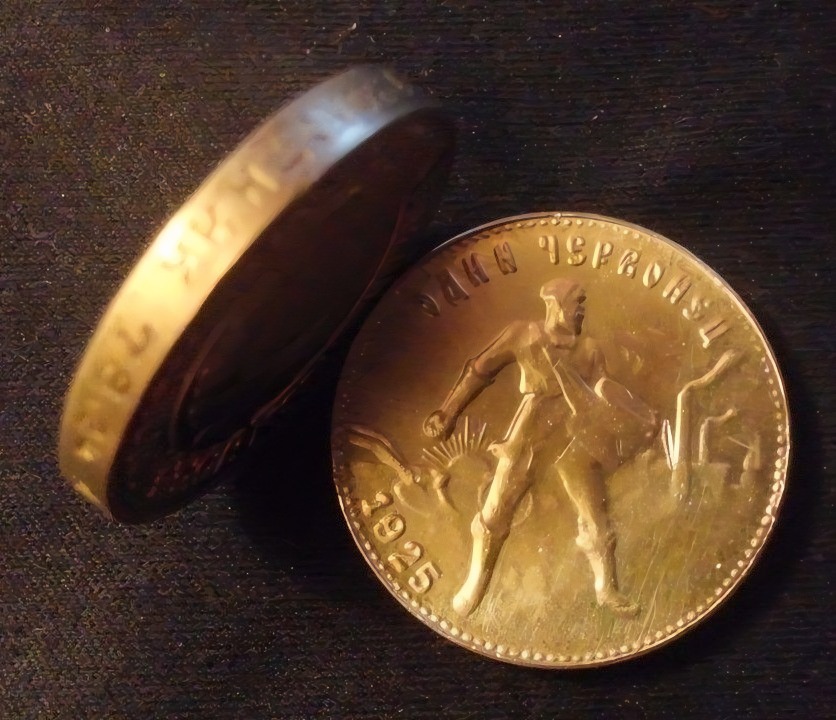
Gold Chevronets
Chervonets is the traditional Russian name for domestic gold coins, including gold rubles.
Chervonets (Chervontsy—plural) are Russian gold coins whose origins date back to the 15th century under Ivan III and were minted sporadically up until the last decade of the Soviet Union; 1982 was the last year the Gold Chervonets were minted.
Originally, the gold coin was identical to the gold ducat, weighing 3.47 grams and 98.6% fine gold. Over the centuries, the coins have ranged in size from 3.47 grams to 1 oz. and in purity from 900 to 999 fine gold.
After the fall of the Soviet Union, the Bank of Russia, under the authority of the Russian Federation, sold off all its old inventory of Soviet Gold Chervonets. In 2006, the Russian Federation introduced new gold and silver bullion coins known as the "Saint George the Victorious," featuring the saint on its reverse side.
Today's Russian Bullion Coins
St. George the Victorious
Gold Russian Bullion Coins
2006 - Present
Saint George the Victorious - Gold Russian Bullion Coin
St. George the Victorious
Silver Russian Bullion Coins
2009 - Present
Saint George the Victorious - Silver Russian Bullion Coin
Other Pages you may like...
|
|
|
|
|
|
Russian Bullion
For Bullion Market News....
Notice:
The charts, commentary, and information on the Free-Bullion-Investment-Guide.com are in no way an endorsement of how you should invest or divest.
|
Support this Guide & Paypal Thank You for Your Support |
|
|
 | |||||
This website is best viewed on a desktop computer.
Keep this Guide Online
& Paypal
Thank You for
Your Support
with Feedly
Search the Guide
| search engine by freefind | advanced |
Premium Canadian Bullion

Give a lasting gift of the iconic Silver Maple Leaf bullion coin [More]
Free Shipping on Orders over $100 (CDN/USA)
or
From the U.K. Royal Mint


Daily
Newsletter
Updated Mintages for
American Gold Buffalo
American Gold Eagle
American Silver Eagle
2024 & 2025
Jerusalem of Gold Bullion
Coin photos
(bottom of page)
Mintages
for
2024
Gold & Silver Mexican Libertad
|
Gold Libertads |
Chinese Gold Coin Group Co.
& Chinese Bullion
Help Us Expand our Audience by forwarding our link
www.free-bullion-investment-guide.com.
Thank You!
Last Month's

In No Particular Order
January 2026
All Articles were Originally Posted on the Homepage