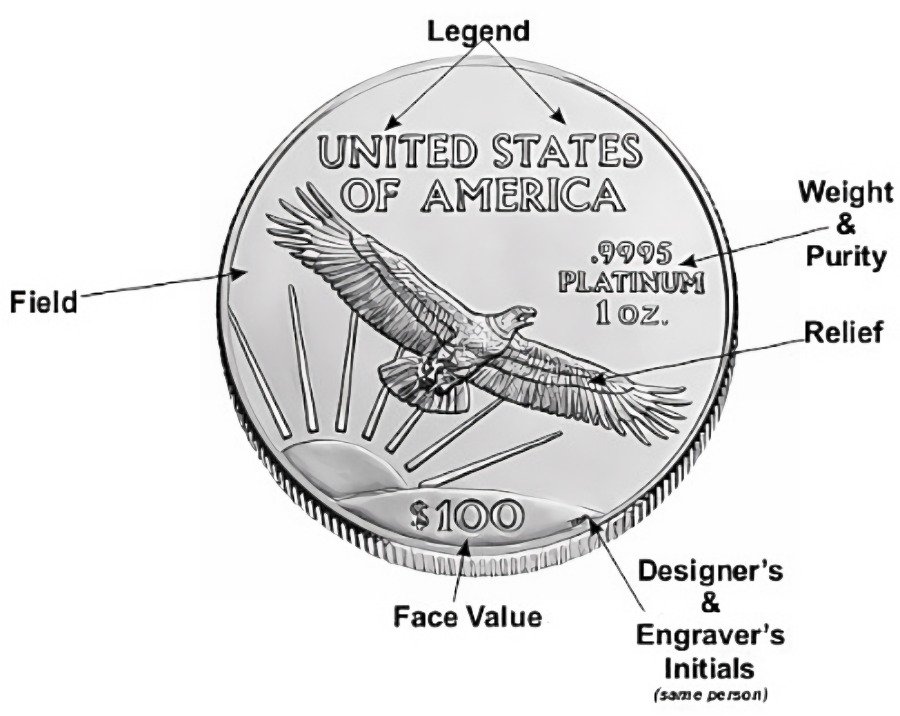
Homepage / AuNP Research Blog / Gold Nanoparticle Cancer Research Report #13
Gold Nanoparticle Cancer Research Report
#13
Originally Posted on 12/19/2019 @ 3:56 pm EST
Last Edited on 3/26/2025
by Steven Warrenfeltz
Hello,
Gold Nanoparticle Cancer Research is a non-invasive cancer treatment that kills cancer without harmful side effects.
In this report, you'll find summaries of the most promising and compelling studies from the past year (2019) in regards to gold nanoparticle medical research.
Below is a glimpse into what you'll find in this report:
- Preliminary Results Released for Naomi J. Halas / Nanospectra’s Nanoparticle Light Therapy for Prostate Cancer
- Harvard Medicine Develops Gold "Nanovehicles" to Suppress Breast Cancer
- Researchers improve CRISPR Delivery with Gold Nanoparticles
- Gold Nanoparticle Delivery of Mesothelioma Drugs has its Advantages over Current Methods
- Dual Therapies become a New Double Action Weapon Against Breast Cancer
First Results from
Naomi J. Halas / Nanospectra’s Gold Nanoshell Light Therapy for Prostate Cancer
Dr. Naomi Halas, a researcher at Rice University, has been conducting experiments on the properties of gold nanoparticles for nearly thirty years.
In November of 2018, Dr. Naomi Halas answered a few questions for a blog post on this site, see it here.
In one of Dr. Halas's answers, she stated that her research is presently in human clinical trials. The research revolved around using gold nanoshells to remove tumors from a man's prostate.
Nanospectra Biosciences is a company founded by Dr. Naomi Halas and bioengineer Jennifer West of Duke University that is providing nanoshells for clinical trials.
Human Clinical Trials
Preliminary Results
The human clinical trials are being conducted by Dr. Rastinehad of Mt. Sinai Hospital in New York and by Steven E. Canfield of UT Health in Houston, TX.
In August of 2019, these preliminary results were reported:
|
The pilot device study reports effectiveness and safety data from Mt. Sinai’s first 16 enrolled subjects diagnosed with localized, low to intermediate risk prostate cancer. After GSN infusion and targeted laser ablation, patients underwent MRI of the prostate at 48 – 72 hours, followed by post-procedure mpMRI/US targeted fusion biopsies at three and 12 months, as well as a standard 12-core systematic biopsy at 12 months. GSN-mediated focal laser ablation was successfully achieved in 94% (15 of 16) patients. At the one-year study endpoint, 87.5% (14/16 lesions) were negative for tumor as confirmed by pathology and considered successful treatment outcomes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) |
Furthermore, Dr. Rastinehad expressed his feelings about the study in the statement below:
|
“The early results are very encouraging and with feasibility study enrollment now complete we anticipate publishing results at the initial three month endpoint for mpMRI targeted fusion biopsies for the entire 45 subject population early next year.” (2020) |
Learn more about this study by following one the two links below:
Nanospectra’s Nanoparticle Light Therapy for Prostate Cancer Shows Promise - biospace
Nanospectra Biosciences Announces PNAS Publication of Initial Results of First Clinical Trial of Gold Nanoshell-Localized Photothermal Ablation of Prostate Tissue - Nanospectra
3/15/22: Rice University professor waits on FDA to approve what she hopes will be a cure for prostate cancer - Eye-Witness News abc13
Harvard Medicine Develops
Gold "Nano Vehicle" to Suppress Breast Cancer
Many cancer therapies affect all of a patient's cells because the drugs cannot differentiate between healthy and cancerous cells. However, in this study, Harvard Medical researchers have found a way around this problem.
Researchers from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have developed a multi-functional gold-nano-vehicle with enhanced drug loading and delivery efficiency capabilities.

The nano-vehicle that Harvard has developed has high loading capacities for both hydrophobic and hydrophilic drugs.
Gold nano-vehicles demonstrated effective drug delivery efficiency in mice, accumulating at tumors after i.v. injection, affecting only cancer cells, not healthy ones.
The triple-drug-loaded gold nano-vehicle successfully delivered its payload to breast cancer in mice, suppressing cancer cells by 94% and 87% at total dosages of 5 mg/kg and 2.5 mg/kg, respectively, through synergy.
Nano-vehicles with nano-gold's photo-thermal properties effectively inhibit multi-drug resistance using near-infrared laser irradiation.
Mingtan Hai, a visiting professor at SEAS and co-author of the study, said the following about the findings in the research.
|
“We can use these hybrid nano-vehicles to deliver a new combination of anticancer drugs in mice through intravenous injection and see remarkable effectiveness against breast tumors.” “This work enables the use of previously undeliverable compounds in cancer therapy and forms a foundation for further development in a broad range of biomedical applications.” - Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences |
To Learn more about this study follow the links below:
New drug delivery system suppresses tumors in mice - Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences
Photothermal-responsive nanosized hybrid polymersome as versatile therapeutics codelivery nanovehicle for effective tumor suppression - PNAS

ExpressGoldCash - 4.9 star - Customer Reviews
Researchers improve CRISPR Delivery with Gold Nanoparticles
Although this research study is not about cancer, it does offer you a glimpse into how science is using Gold Nanoparticles to make CRISPR more efficient.
'CRISPR' stands for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats. It is a genome-editing tool that is centered on splicing DNA.
In this next study, a team of researchers from Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center improved the delivery of CRISPR with Gold Nanoparticles to edit genes related to HIV and sickle cell anemia.

CRISPR-Cas9 has had many good results in several lab-controlled research studies; however, one big issue with CRISPR is getting it to its expected destination in a living specimen.
Furthermore, researchers have found that the longer the CRISPR-Cas9 DNA-editing tool is in the body, it becomes a threat to the body because it could make unwanted 'edits.'
In this study, researchers loaded gold nanoparticles with the CRISPR gene-editing tool, allowing the nanoparticles to deliver and deposit CRISPR into blood stem cells.
After CRISPR's delivery was made, it altered genes related to HIV and certain blood disorders. Researchers said that "it’s a promising step toward addressing CRISPR’s critical delivery problems."
Senior scientist Dr. Jennifer Adair of Fred Hutchinson stated the following about using gold nanoparticles for the delivery of CRISPR.
|
"As efficient couriers, they (gold nanoparticles) could reduce the need for engineered viruses and specialized research centers. And that could help make these emerging, high-tech treatments accessible and affordable." “Gene therapy has a lot of potential across many diseases, but the process we have right now is just not feasible in every place in the world.” “We want to end up delivering gene therapy in a syringe. This gold nanoparticle represents the first possibility we have to do that for blood stem cells.” - Dr. Jennifer Adair of Fred Hutchenson |
To Learn more about this study from Fred Hutchenson, 'click' this link: Special delivery: Gold nanoparticles ship CRISPR cargo - Fred Hutch.org
Gold Nanoparticle Delivery of Mesothelioma Drugs has its Advantages over Current Methods
Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is a rare but very aggressive form of cancer.
 Mesothelioma in a lung
Mesothelioma in a lungPemetrexed (Pe) is a rare chemotherapy drug used to combat cancer, despite its limited effectiveness.
In this study, researchers in Italy used gold nanoparticles to help Pemetrexed (Pe) to be more effective at stopping this rare form of cancer.
The study revealed that the administration of gold nanoparticles with Pemetrexed (Pe) significantly reduced the cell viability and mobility of cancer cells. Below are notes taken from the researcher's experiments; they found that gold nanoparticles greatly enhanced the chemo drug's effectiveness:
- Dove Press |
The study's results were as follows:
- Dove Press |
The research findings can be further accessed through the provided links.
Gold Nanoparticle Delivery of Mesothelioma Drugs Shows Significant Advantage - Mesothelioma.netPemetrexed-loaded nanoparticles targeted to malignant pleural mesothelioma cells: an in vitro study - Dove Press
Dual Therapies become a
New Double Action Weapon Against Breast Cancer
In this last study, researchers from the University of Delaware devised an effective way to fight triple-negative breast cancer. Triple-negative breast cancer is a form of breast cancer that accounts for 10 to 20 percent of patients.
University of Delaware researchers Emily Day and Joel Rosenthal have combined two minimally invasive therapies to become a new powerful weapon against this type of breast cancer.
The short video below offers an animated and informative explanation of Dr. Day and Rosenthal's research.
See the full article about the University of Delaware's Research here: NEW WEAPON AGAINST BREAST CANCER - The University of Delaware
Thank You for your Time.
Take Care & God Bless,
Steve
Other pages, on this Guide, that you
may like...
Notice:
The charts, commentary, and information on the Free-Bullion-Investment-Guide.com are in no way an endorsement of how you should invest or divest.
|
Support this Guide & Paypal Thank You for Your Support |
|
|
 | |||||
This website is best viewed on a desktop computer.
Keep this Guide Online
& Paypal
Thank You for
Your Support
with Feedly
Search the Guide
| search engine by freefind | advanced |
Premium Canadian Bullion

Give a lasting gift of the iconic Silver Maple Leaf bullion coin [More]
Free Shipping on Orders over $100 (CDN/USA)
or
From the U.K. Royal Mint


Daily
Newsletter
Updated Mintages for
American Gold Buffalo
American Gold Eagle
American Silver Eagle
2024 & 2025
Jerusalem of Gold Bullion
Coin photos
(bottom of page)
Mintages
for
2024
Gold & Silver Mexican Libertad
|
Gold Libertads |
Chinese Gold Coin Group Co.
& Chinese Bullion
Help Us Expand our Audience by forwarding our link
www.free-bullion-investment-guide.com.
Thank You!
Last Month's

In No Particular Order
January 2026
All Articles were Originally Posted on the Homepage